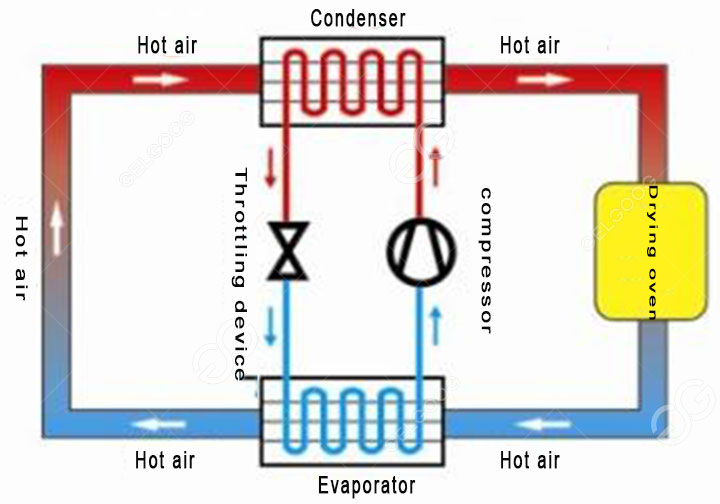
The heat pump dryer is to use the reverse Carnot principle to absorb the heat of the air and transfer the heat to the drying room, and then through the heat pump host to increase the temperature in the drying room. The heat pump dryer is composed of compressor-heat exchanger (internal machine)-throttle-heat absorber (outer machine)-compressor and other devices constitute a circulating system.
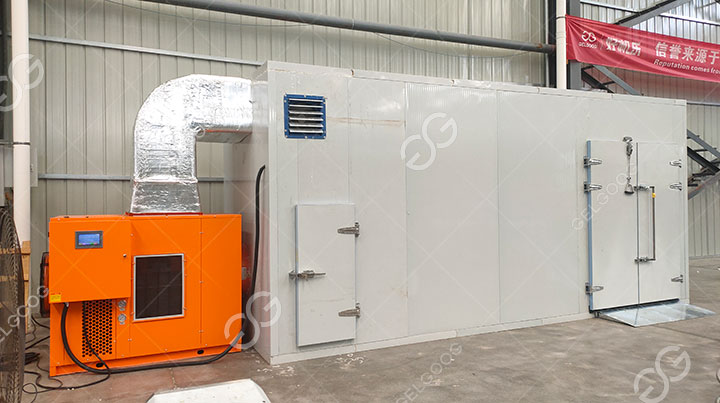

The heating process of the heat pump dryer system: during the drying process of our materials, the outside high temperature heat pump will cyclically heat the drying room. When the temperature reaches our pre-set value, the heat pump host next to it will It will stop running, and when the temperature in the drying machine room is lower than our specified temperature, the heat pump host will be automatically activated to heat the drying room.
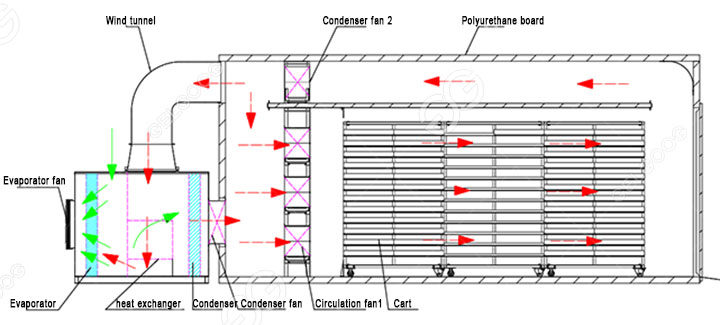
Dehumidification process: The dehumidification system of the heat pump dryer is also automatic, which is determined by the temperature. When you set the temperature to 60 degrees Celsius and the humidity to 80%, when the environment of the drying room reaches such a predetermined value At that time, the dehumidifying fan will automatically turn on, and the water vapor drawn by the exhaust fan will be introduced into the heat pump room into the drain along with the airflow. If the ambient temperature and humidity of the drying room are lower than the set value, the exhaust fan will be automatically activated. closure.
Cold air recovery: The heat pump host will discharge cold air when it is in operation. The temperature is generally 5-10 degrees Celsius lower than normal temperature. Then the cold air will be introduced into the production workshop to cool down for use.
What causes the low thermal efficiency of the air-energy heat pump drying mechanism?
1. Low heating temperature
The heating temperature of air source heat pump units is generally around 55 degrees, because the higher the heating temperature requirements, the slower the temperature rise in the high temperature section, the significant decrease in heating efficiency, and the increase in energy consumption of air source heat pump units. Therefore, in the case of meeting the conditions of use, try to lower the target water temperature as much as possible, and use the air source heat pump rationally.
2. Low condenser fouling efficiency
Low-temperature refrigerant enters the evaporator to exchange heat with the air. If the air is dusty, the dust in the evaporator after long-term use will affect the heat exchange efficiency of the air source heat pump unit. Soap water can be used to clean the evaporator; when the quality of tap water or underground water is poor, the compressor When the produced high-temperature refrigerant exchanges heat with the condenser, the condenser coil will become fouled, the thermal conductivity will decrease, the heat exchange efficiency will decrease, and the heat accumulation in the compressor will cause high-pressure protection.
3. Low heating efficiency at low temperature
When the working environment temperature of the unit is lower than 5 degrees, the air source heat pump unit will defrost once every hour. The default defrost time is 10 minutes. Generally, the four-way valve is used to change the direction of the refrigerant. The high-temperature refrigerant produced by the compressor directly enters the evaporator to defrost. , The air source heat pump unit is converted from heating to cooling, which increases power consumption.
For more professional questions about heat pump dryers, please feel free to consult us!!
